GPIO Edge Trigger
This example demonstrates defining a custom Lambda Trigger that subscribes to GPIO edge events via the Linux kernel. It then demonstrates various Lambdas that respond to it and perform various functions.
Initial Provisioning
graph LR; cli --> control_plane; console --> control_plane; control_plane <-- tunnel --> agent; subgraph user_edge[User Edge] cli[CLI]; console[Console]; end subgraph cloud[Cloud <small>api.on-prem.net</small>] control_plane[Control Plane]; end subgraph device_edge[Device Edge] agent[Agent]; end
Subsequent Autonomous Edge Operation
graph TB; agent --> trigger[Lambda Trigger]; pin -- edge trigger --> trigger; trigger --> lambda1; trigger --> lambda2; trigger --> lambda3; subgraph device_edge[Device Edge] agent; pin[GPIO Pin]; end subgraph agent[Agent] trigger; lambda1[Lambda 1]; lambda2[Lambda 2]; lambda3[Lambda 3]; end
Define the lambda trigger
$ onprem generate xid
cj7ca3berad6gieb3rbg
# my_gpio_trigger_type.yaml
id: cj7ca3berad6gieb3rbg
kind: LambdaTriggerType
name: gpio_trigger
description: >
Trigger lambdas when a GPIO edge event occurs.
runsAtControlPlane: false
runsAtDevices: true
scriptContentType: text/x-lua
script: >
local GPIO = require('periphery.GPIO')
local socket = require('socket')
local M = {}
function M.init(context)
local params = {
path = '/dev/gpiochip0',
line = 23,
direction = 'in',
edge = 'both',
}
local gpio = GPIO(params)
context['gpio'] = gpio
end
function M.run(context)
local gpio = context.gpio
while true do
local event = gpio:read_event()
coroutine.yield(event)
socket.sleep(0.005)
end
end
return M
The sleep used above is precautionary but unnecessary when performing a blocking call such as
read_event(). Each Lambda Trigger loop runs in a dedicated thread, and run loops are
free to peg the CPU of a single core if they want.
Upload it to the control plane
$ onprem apply ./my_gpio_trigger_type.yaml
It will now show up in the cloud console.
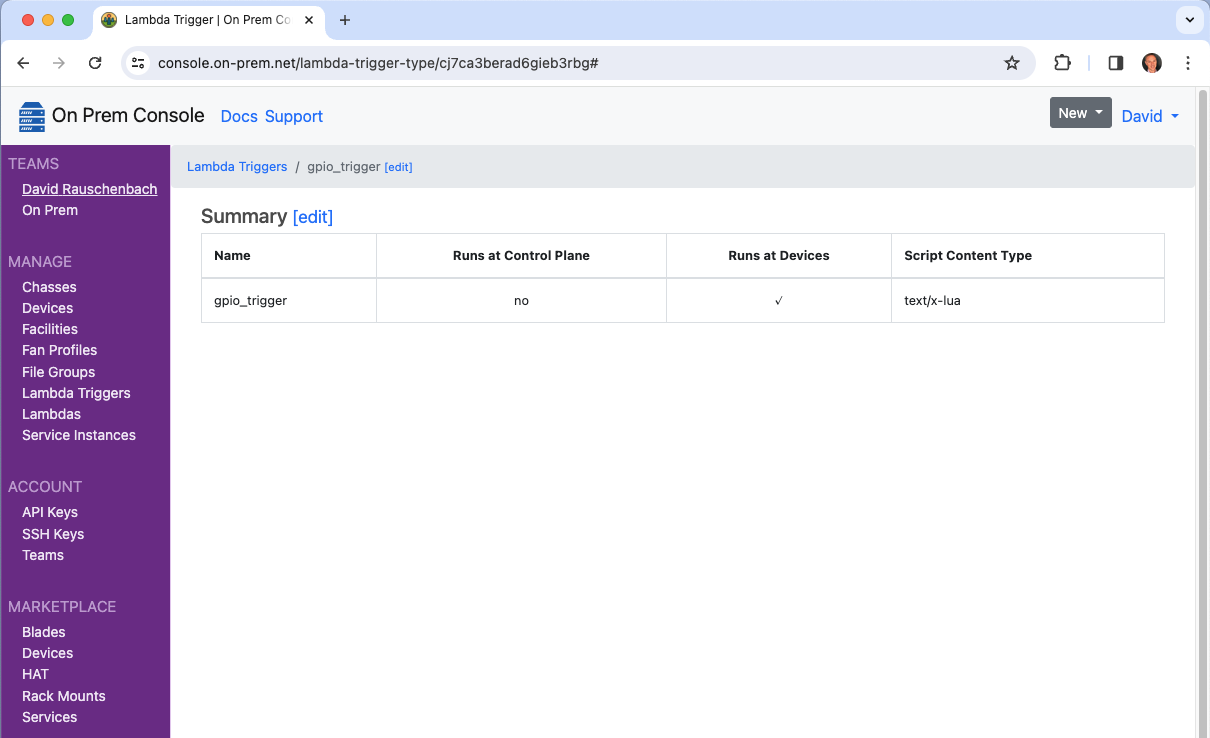
And it will also now show up as one of the trigger choices when editing a Lambda.
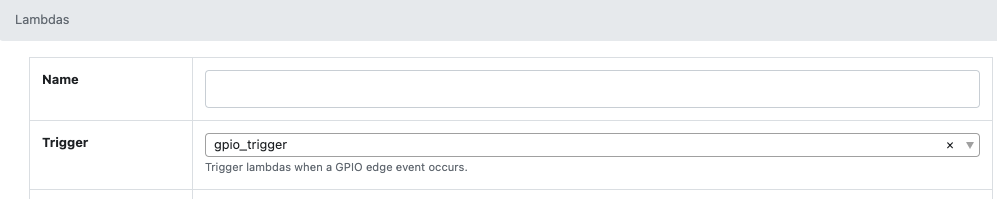
Lambda Example 1: Configure an LED to follow the GPIO pin
$ onprem generate xid
cj7co6jerad78frcc100
# follow_gpio23_with_led0.yaml
id: cj7co6jerad78frcc100
kind: Lambda
name: follow_gpio_with_led0
description: >
Follow GPIO pin 23 and display with led0.
runAt:
deviceId: ci2fabp32ckvhk1g9qe0
triggerTypeId: cj7ca3berad6gieb3rbg
scriptContentType: text/x-lua
script: >
local LED = require('periphery.LED')
local led = LED('led0')
local M={}
function M.handler(event, context)
local newValue = false
if event.edge == 'rising' then
newValue = true
end
led:write(newValue)
return {edge=event.edge, timestamp=event.timestamp}
end
return M
$ onprem apply ./follow_gpio23_with_led0.yaml
Lambda Example 2: Aggregate the GPIO events in Redis
$ onprem generate xid
clv0p4u56a1fjkem7h9g
# follow_gpio23_and_aggregate_in_redis.yaml
id: clv0p4u56a1fjkem7h9g
kind: Lambda
name: follow_gpio23_and_aggregate_in_redis
description: >
Follow GPIO pin 23 and aggregate events in Redis.
runAt:
deviceId: ci2fabp32ckvhk1g9qe0
triggerTypeId: cj7ca3berad6gieb3rbg
scriptContentType: text/x-lua
script: >
local redis = require('redis')
local redisClient = redis.connect('my-redis', 6379)
assert(redisClient:ping())
local M={}
function M.handler(event, context)
redisClient:pipeline(function(pipeline)
-- Count total events for all time
pipeline:incrby('event_count', 1)
-- Also count events per day
pipeline:incrby('event_count_' .. os.date('%Y-%m-%d'), 1)
-- Also count events per hour
pipeline:incrby('event_count_' .. os.date('%Y-%m-%dT%H'), 1)
end)
return {edge=event.edge, timestamp=event.timestamp}
end
return M
$ onprem apply follow_gpio23_and_aggregate_in_redis.yaml